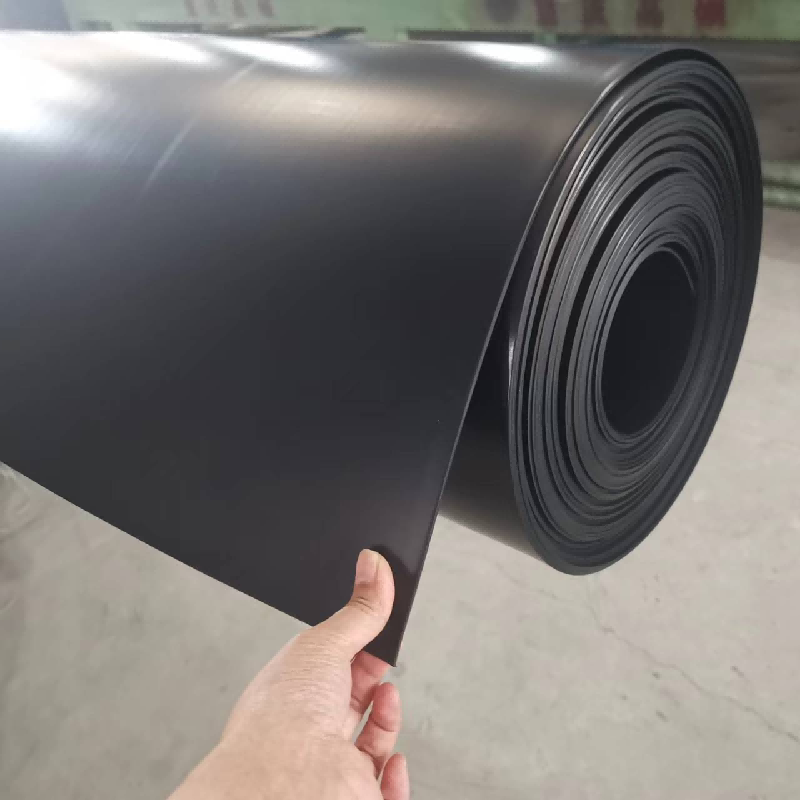
High Density Polyethylene Geomembrane
HDPE geomembrane is a high-performance waterproof material made from premium polyethylene resin. It offers excellent tensile, tear, and puncture resistance, along with strong chemical corrosion and UV stability. Ideal for landfills, tailing ponds, and water conservancy projects, it ensures long-term impermeability and reliable performance in harsh environments through thermally fused seams.
product presentation
High density polyethylene geomembrane is one of the geosynthetic materials, the application of geosynthetic materials originated in the 1950s, a waterproof barrier material produced with high density polyethylene resin as raw material (geomembrane with density of 0.94g/cm3 or above).
Product features
1. Made without chemical additives and heat-treated, this is a type of building material.
2. Features excellent mechanical properties, good water permeability, corrosion resistance, and aging resistance.
3. Exhibits strong anti-burial and corrosion resistance with a porous structure that ensures superior drainage performance.
4. Possesses high friction coefficient and tensile strength, demonstrating geosynthetic reinforcement capabilities.
5. Provides functions including isolation, filtration, drainage, protection, stabilization, and reinforcement.
6. Adapts to uneven subgrade surfaces while resisting construction-induced damage with minimal creep.
7. Offers excellent continuity, lightweight design, and easy installation.
8. As a permeable material, it provides outstanding filtration and isolation functions with strong puncture resistance, ensuring robust protective performance.
product use
Mainly used in landfill, sewage and waste liquid treatment, water conservancy, agriculture, transportation, high-speed railway, tunnel, airport, airport, building, landscape and other anti-leakage liner engineering.
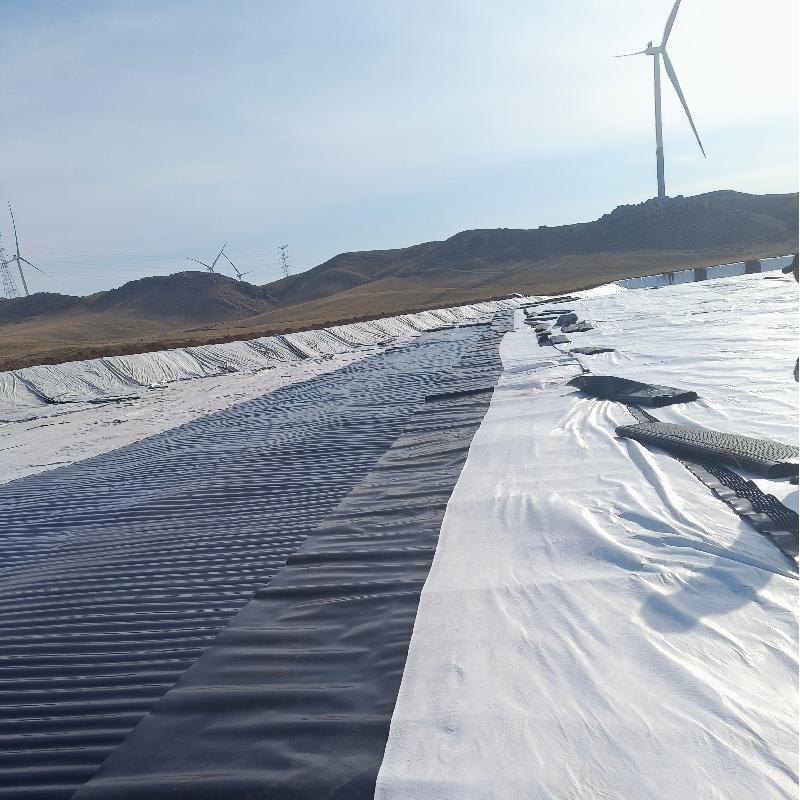

Construction plan specification
During transportation, avoid dragging or forcefully pulling the geotextile membrane to prevent puncture by sharp objects.
1. Lay the membrane from the base upward, maintaining a 1.50% slack allowance for localized settlement and stretching. Considering the project's specific conditions, slopes should be laid vertically from top to bottom;
2. Longitudinal joints between adjacent layers must be offset by at least 1 meter horizontally;
3. Longitudinal joints should be positioned 1.50 meters above dam footings and bends, and installed on flat surfaces;
4. Prioritize slope construction over field base installation;
5. When laying slopes, ensure the membrane orientation aligns parallel to the steepest slope line.