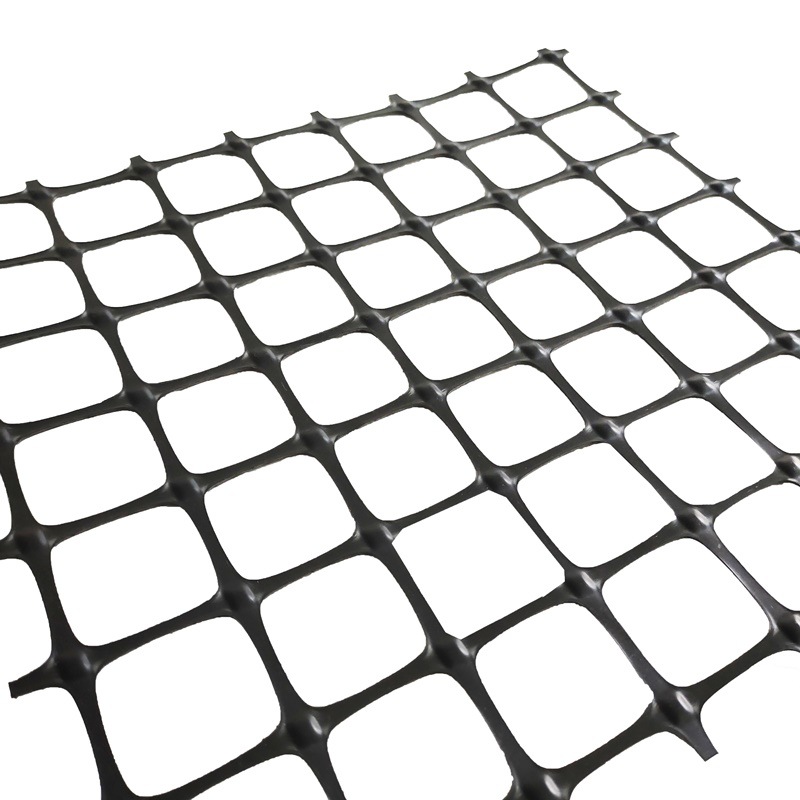
Geogrid
Geogrids are grid-like geosynthetics made from polymers (e.g., HDPE, PP) or composites, designed to reinforce soils, distribute loads, and stabilize structures in civil engineering. Key variants include polymer (uniaxial/biaxial), steel-plastic (high-strength), and fiberglass (asphalt-compatible) geogrids. They enhance soil shear strength, reduce settlement, and prevent cracks in applications like roads, railways, landfills, and coastal protection. Notable for durability (50+ years), lightweight installation, and cost efficiency, they minimize material use and carbon footprint. Innovations include biodegradable options for eco-friendly projects. geogrids ensure reliable performance across diverse terrains and extreme conditions, balancing economic and environmental goals.
Geogrid Product Introduction
1. Definition & Overview
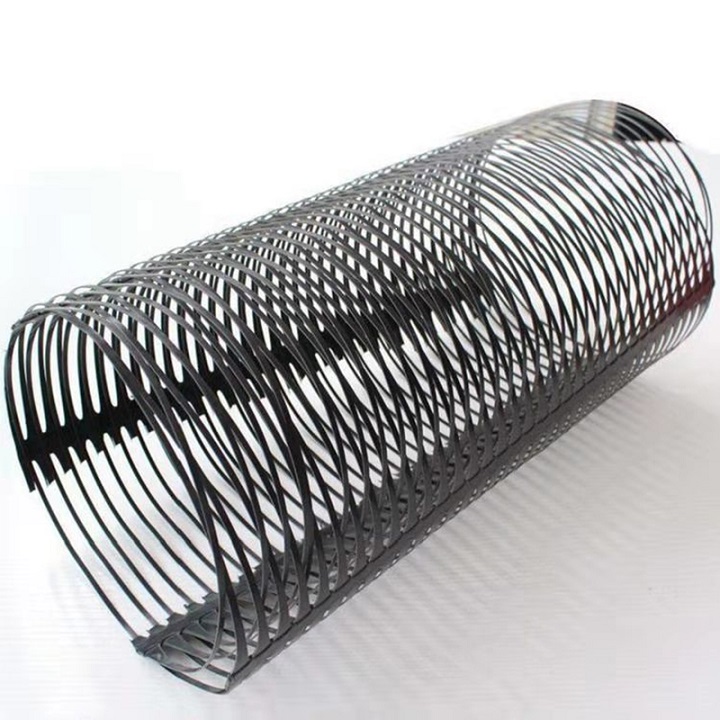
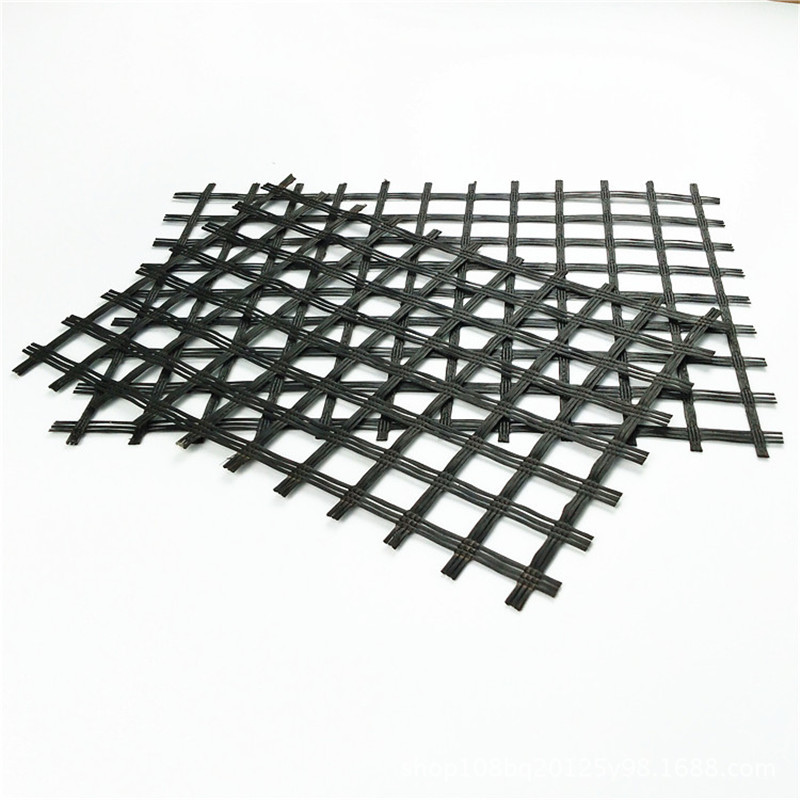
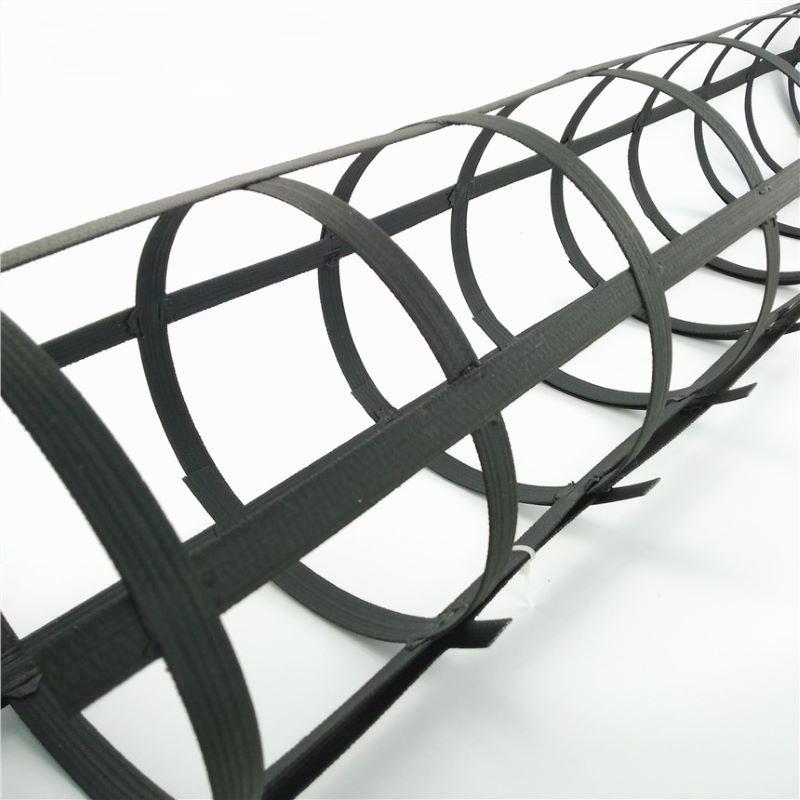
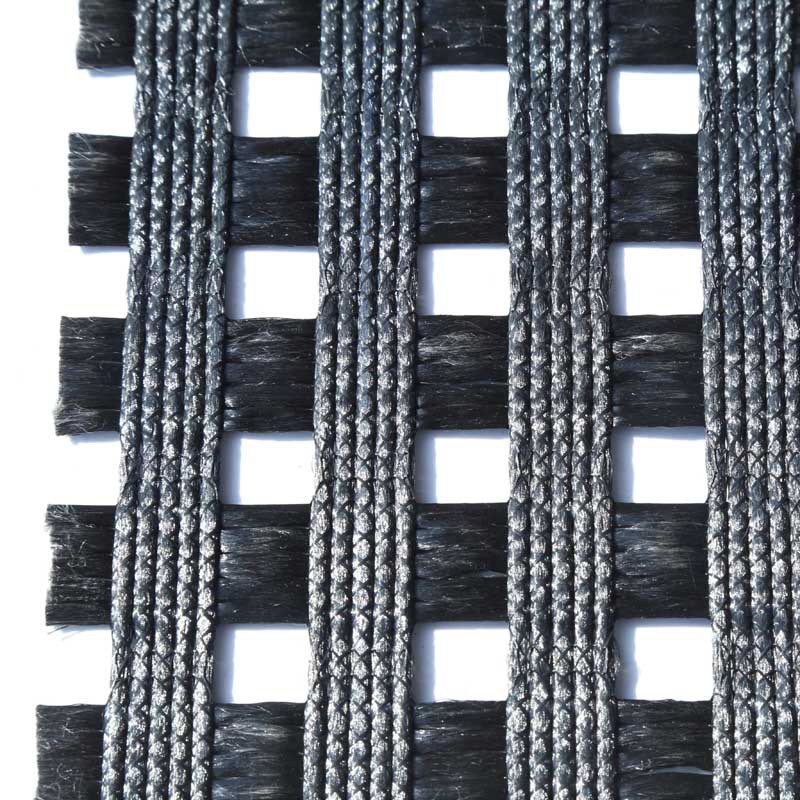
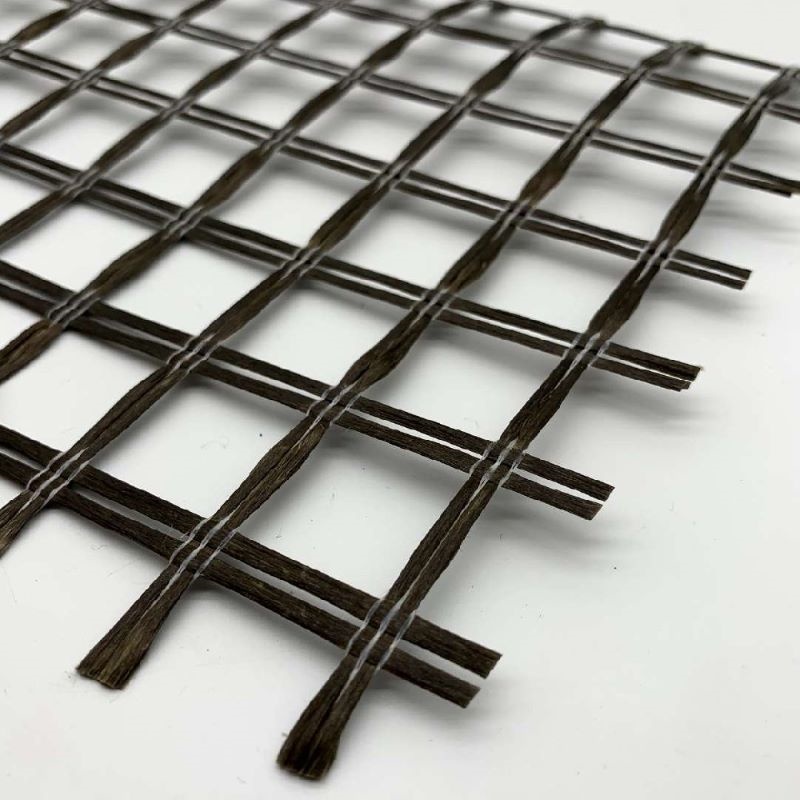
Geogrid is a grid-like geosynthetic material made from polymers (e.g., polyester, polyethylene, polypropylene) or composite materials. It is primarily used in civil engineering for soil reinforcement, load distribution, and structural stabilization. Its unique open-grid structure interlocks with soil and aggregates, enhancing tensile strength and structural integrity.
2. Key Types & Features
Based on material and manufacturing processes, geogrids are categorized as follows:
Polymer Geogrids
Material: High-density polyethylene (HDPE) or polypropylene (PP).
Features: Corrosion-resistant, acid/alkali-tolerant, lightweight; ideal for soft soil stabilization and roadbed reinforcement.
Common Forms: Uniaxial (enhanced unidirectional strength) or biaxial (balanced bidirectional strength).
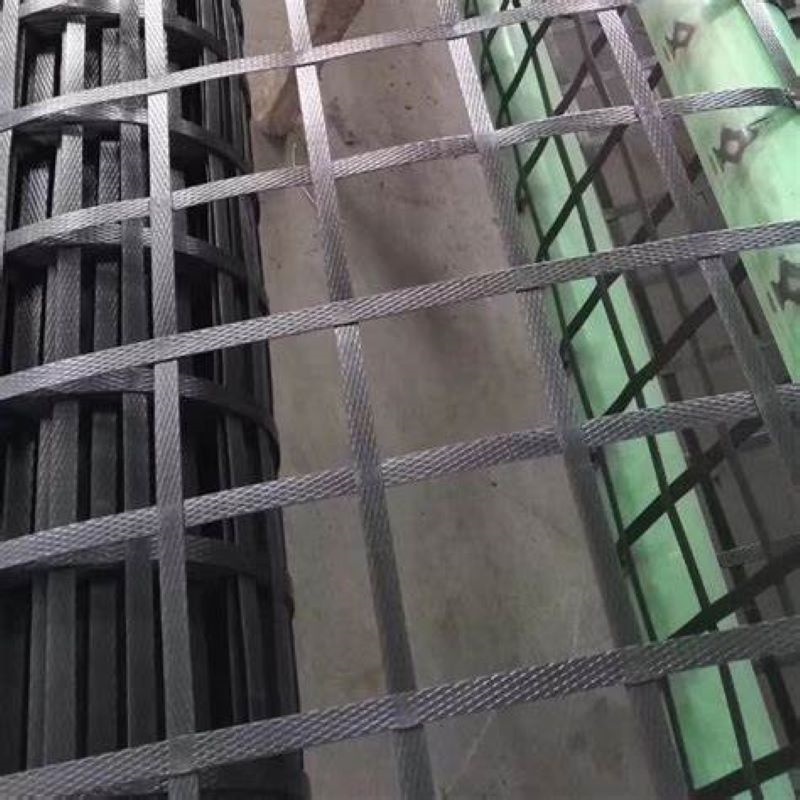
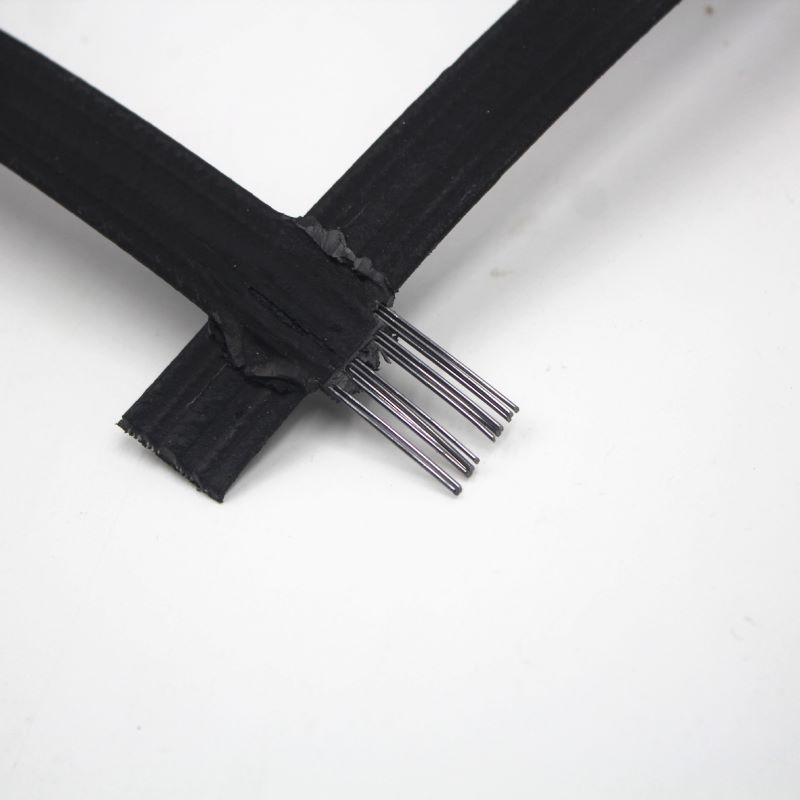
Steel-Plastic Composite Geogrids
Material: Steel wire core coated with polyethylene.
Features: Ultra-high tensile strength (exceeding 100kN/m), excellent creep resistance; suitable for heavy-load applications (e.g., railways, airport runways).
Fiberglass Geogrids
Material: Fiberglass mesh with asphalt coating.
Features: High-temperature resistance, anti-aging; designed for asphalt pavement reinforcement to reduce rutting and cracking.
3. Core Functions
Soil Reinforcement: Enhances soil shear strength via mechanical interlock, preventing landslides or collapses.
Load Distribution: Evenly disperses vertical loads to minimize differential settlement (e.g., in road subgrades).
Separation & Filtration: Isolates dissimilar soil layers while allowing water permeability (e.g., in landfill liners).
Tension Resistance: Absorbs tensile stresses in flexible structures (e.g., retaining walls, reinforced slopes) to limit deformation.
4. Typical Applications
Transportation: Highway/railway subgrades, airport runways, parking lot foundations.
Hydraulic Engineering: Riverbank/coastal protection, reservoir slopes, drainage trench reinforcement.
Municipal Engineering: Landfill base layers, underground pipeline protection, landscape retaining walls.
Mining & Energy: Mining access roads, oil tank foundations, pipeline supports.
5. Product Advantages
Efficient Installation: Lightweight and easy to deploy, enabling mechanized construction and shorter timelines.
Longevity: UV-resistant, chemically inert, with a service life exceeding 50 years.
Cost-Effective & Eco-Friendly: Reduces reliance on stone/concrete, lowering costs and carbon footprint.
Versatility: Adapts to complex terrains (e.g., swamps, slopes) and extreme climates.
6. Installation Guidelines
Site Preparation: Level the ground and remove sharp debris.
Orientation: Align the primary strength direction of the geogrid perpendicular to expected loads.
Connection: Secure overlaps (≥15cm) using specialized connectors or stitching to prevent displacement.
Backfilling: Compact soil/aggregate in layers to ensure full interlock with the geogrid.
7. Selection Guide
Low-Load Scenarios (e.g., green slopes): Opt for uniaxial polymer geogrids.
High-Load Scenarios (e.g., heavy-duty pavements): Prioritize steel-plastic composite geogrids.
Pavement Crack Prevention: Use fiberglass geogrids with asphalt coatings.
8. Standards & Market Trends
International Standards: Complies with ASTM, ISO, etc., ensuring tensile strength, elongation, and other parameters meet specifications.
Innovation: Recent advancements include biodegradable geogrids (plant-based fibers) for temporary projects or ecological restoration.